Welding stainless steel is difficult because the material has a high resistance to heat and corrosion. The high resistance to heat will cause the weld to be very hot, which can cause distortion and damage to the metal. The corrosion resistance also makes it difficult to weld with consistent quality.
14 Cases
Considered
110 Hours of Research
7 Experts Interviewed
10 Articles
Analyzed
Stainless steel is a popular material for many reasons – it’s corrosion-resistant, has a high strength-to-weight ratio, and doesn’t corrode in wet environments.

But welding stainless steel can be a difficult process – the metal doesn’t respond well to heat and can be brittle. In this article, we’ll take a look at some of the reasons why welding stainless steel is so difficult, and discuss some ways to make the process easier.
Types Of Stainless Steel
When it comes to welding stainless steel, there are a few things to keep in mind. First of all, stainless steel is a type of steel that is highly resistant to corrosion.
This means that it’s difficult to weld without first prepping the metal with a treatment that helps prevent the weld from breaking. Secondly, stainless steel is a relatively soft metal and requires a different approach when welding than other types of metals.
Finally, because stainless steel is so difficult to weld, it’s important to use the right equipment and techniques when working with this material.
The Different Types Of Welds That Can Be Made
Welding stainless steel is difficult because the metal has a high resistance to heat and corrosion. Three types of welds can be made: gas, arc, and plasma.
Gas welding is the most common type of welding used with stainless steel because it is a fast and easy process. The welding gases are heated until they reach a temperature of around 700 degrees Fahrenheit. This high temperature melts the metal together and forms a weld.

Arc welding is similar to gas welding, but the welding arc is instead of a gas. The arc is created by using an electric current and it heats the metal until it melts.
This type of weld is more durable than gas welding, but it is also more difficult to learn because you need to know how to correctly use the arc.
Plasma welding is a new type of welding that uses an ionized gas called plasma. Plasma welding is faster than other types of welds, but it also has less resistance to heat and corrosion. It is also easier to learn than other types of welds because you do not need an arc or a welder’s torch.
The Grain Structure Of Stainless Steel
The grain structure of stainless steel makes it difficult to weld. The metal tends to form martensite, which is a hard, brittle form of steel. This makes it difficult to weld without causing damage to the metal.
Stainless steel also has a high amount of nickel, which makes it difficult to weld without creating sparks. This means that stainless steel is not the best material for welding in areas where sparks are a concern.
Overall, the grain structure of stainless steel makes it difficult to weld, which is why it is commonly used in items that don’t require a lot of repair or maintenance.
How Welding Stainless Steel Affects The Material Properties?
The high resistance to heat and corrosion can also cause the weld to be brittle, which makes it difficult to form a strong joint. The high resistance also means that the weld will not take on a uniform shape, which can lead to defects in the metal.
The Heat Treatment Process For Stainless Steel
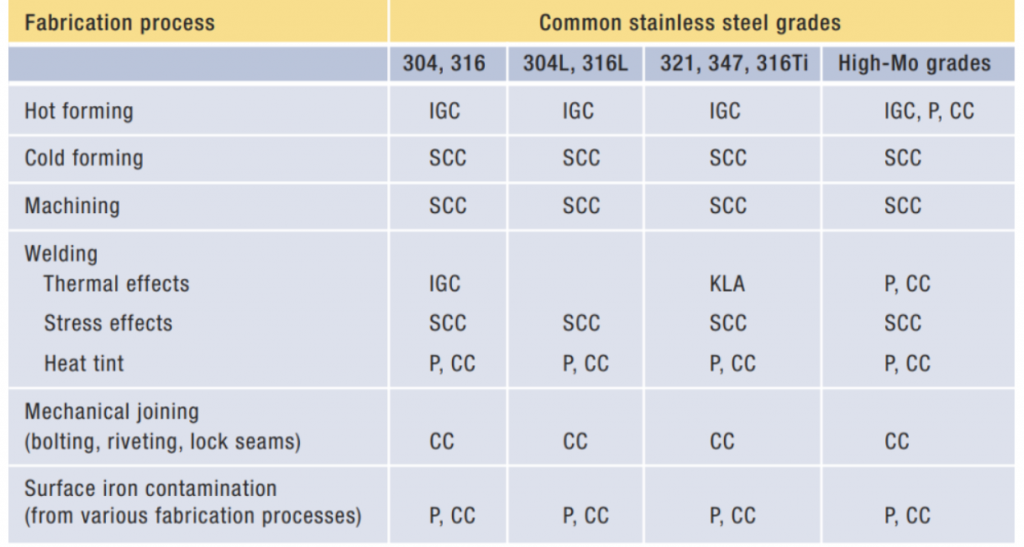
When welding stainless steel, it is important to understand the different heat treatments that can be done to the metal. Each of these treatments has its benefits and drawbacks and must be taken into account when welding stainless steel.
One of the most common methods of welding stainless steel is gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW). GTAW is a reliable process, but it can be difficult to weld stainless steel because of its high resistance to heat.
To overcome this problem, many welders use a filler metal, such as chrome-molybdenum alloys, to help increase the heat penetration into the stainless steel.
Other methods of welding stainless steel include shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) and submerged arc welding (SAW). SAW is a more expensive process than GTAW, but it offers greater precision and control. Shielded metal arc welding (SMEW) is similar to GTAW, but the welder uses an electric arc instead of a gas tungsten arc.
Each method of welding has its own set of benefits and drawbacks and must be considered when selecting a welding procedure for Stainless Steel.
The Challenges Of Welding Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is a popular material for many applications, but welding it is often difficult. The metal is resistant to many common welding processes, including arc welding and butt welds. Here are some of the reasons why welding stainless steel can be tricky:
- Stainless steel has a high resistance to heat, so it requires a higher heat input to weld successfully.
- Stainless steel doesn’t spark when welded, so electrodes must be made with special materials that resist sparking.
- The metal is also difficult to work with because it’s brittle and has a low melting point. These factors make it difficult to create consistent welds with less distortion.
- Stainless steel has low corrosion resistance, so it needs special care when welding in wet environments.
- The metal is also difficult to weld because it’s often too thin or has irregular contours. These factors can make it difficult to create a strong joint.
- Stainless steel is difficult to machine, so it can be challenging to create welds that are uniform in thickness. This can lead to distorted joints and decreased performance.
- Stainless steel is also sensitive to impurities in the weld, so it requires careful cleaning and inspection before welding.
- Stainless steel requires special welding techniques, such as arc welding, to prevent corrosion and distortion.
- The metal is also prone to galling, which is a phenomenon where the metal’s surface becomes detached from the underlying substrate. Galling can lead to cracks in the weld, which can significantly impact the overall performance of the piece.
- Stainless steel is often difficult to paint or finish after welding, due to the metal’s harshness and susceptibility to rust.
Common Stainless Weld Defects & How To Fix Them
Below are some of the most common stainless steel weld defects, along with some tips for fixing them.
Hot Cracking
The term “hot cracking” refers to the problem of stainless steel going above its maximum temperature before cooling down. This results in cracks appearing on the joints, as the stainless steel cools down. Over time, the cracks may grow, which can lead to the weld falling apart.
Hot cracking can be avoided by using the right filler material while welding, preheating your joints, and avoiding lower currents. Make sure that your welder is set correctly as well.
Porosity
Weld porosity is a defect of the weld, where bubbles are trapped inside the weld, which is something you will want to avoid when you weld.
To fix that, make sure that your base metal is properly cleaned. Keep track of your joint and make sure it is dry. Make sure your welder is set properly.
Deformation
Deformation occurs frequently when welding stainless steel, mainly due to the fact that stainless steel retains heat quite well. As a result, stainless steel is usually prone to deformation after welding.
You can avoid this problem by welding the metal from both sides to prevent it from deforming.
Conclusion
Welding stainless steel is difficult for several reasons. First, the metal has a high resistance to heat and therefore requires a higher welding temperature than other types of steel.
Second, stainless steel is also very brittle and does not hold an edge well, which makes it difficult to weld without distortion or warping.
Finally, because stainless steels are so resistant to rust and corrosion, they require special techniques when welding in humid environments or with corrosive gases such as chlorine.
By understanding some of the challenges associated with welding stainless steel, you can make the process easier. For example, using a filler metal can help increase the heat penetration into the metal and reduce the need for extra welds. Additionally, using specific welding procedures can help reduce the risk of corrosion or distortion.