The main difference between MIG and TIG is the way the arc is used. The term MIG (metal inert gas) refers to welding that uses a feed wire that constantly moves through the gun and generates a spark. The wire melts to complete the weld. For TIG (tungsten inert gas) welding, a long rod is used to fuse two metals together directly.
115 Cases
Considered
200 Hours of Research
20 Experts Interviewed
112 Articles
Analyzed

Using the correct welding technique ensures that a wire basket can hold together under load. However, using the wrong welding technique can lead to many problems, such as B. Weaker joints, corrosion of the weld joint, or not completing the weld at all.
MIG and TIG welding both use an arc to make the weld. The difference between the two is the way the bow is used. In TIG (inert tungsten gas) welding, two metals are directly fused utilizing long rods.
Two of the most common welding techniques used in plants in the United States are inert gas (MIG) and TIG (tungsten inert gas) welding.
Both arc welding techniques have their similarities, but there are times when one is more useful than the other. So how do you know when to use MIG vs TIG welding?
MIG vs. TIG Welding : What is MIG welding?
MIG or metal inert gas welding is a process in which a metal wire is continuously inserted into the weld seam. The consumable welding material of the wire acts as filler material to bond the two metal objects together.
To prevent the workpiece from slipping while welding and potentially affecting the angle of the joint, a block of wood is cut with a wood milling machine, which is commonly used to brace the joint.
Then the robot welder moves the welding arm precisely and quickly to evenly distribute the heat after the weld is complete.
What does MIG stand for in welding?
MIG welding is an arc welding method in which a consecutive solid wire electrode is fed through a welding gun and, MIG stands for metal inert gas.
How MIG Weld?

The gas mixture used in MIG welding must be different from that used in TIG welding. You don’t want a completely inert protective gas like 100% helium. The arc properties of the MIG process, which uses filler, are very different from the processes in the TIG welding process. Using the wrong gas would, therefore, adversely affect the efficiency of the arc weld.
MIG Welding Procedure
The MIG welder must be properly cleaned after the welding process is complete. A side effect of using a filler material is that a weld seam can cause weld spatter no matter how fast the welder is.
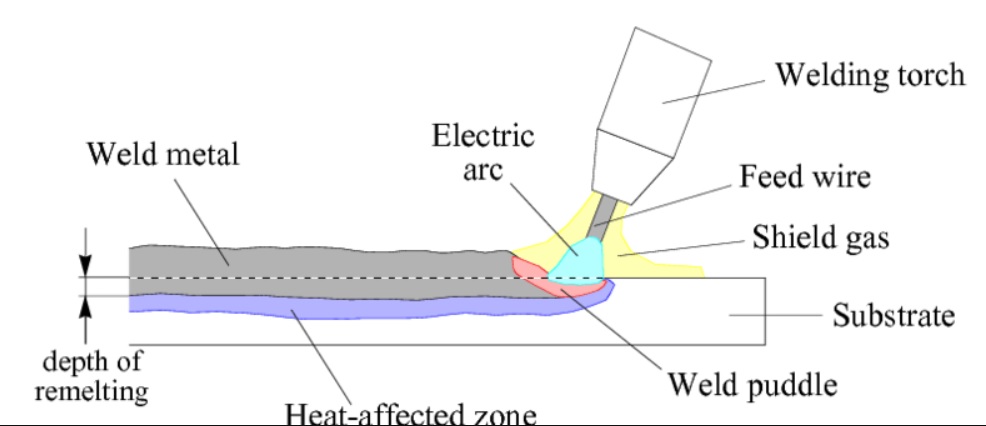
Since the spatter can sometimes cause burrs on the weld joint, which can potentially lead to injury, an additional step of grinding or electroplating may be required to remove these “spatter burrs”.
Advantages and Disadvantages of MIG and TIG Welding
Both MIG and TIG welding have their own strengths and weaknesses, depending on the type of metal, the thickness of the material, the joint configuration, the quality requirements, the cost factors, and the personal preference of the welder. Here are some of the main advantages and disadvantages of each process:
MIG Welding Advantages
- It is faster and more productive than TIG welding, as it can deposit more metal in less time.
- It is easier to learn and perform, as it does not require much skill or coordination from the welder.
- It can weld thicker materials with less distortion and less heat input.
- It can weld a wide range of metals, such as carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper, nickel, etc.
- It can weld in different positions, such as flat, horizontal, vertical, or overhead.
MIG Welding Disadvantages
- It produces more spatter and slag than TIG welding, which need to be cleaned after welding.
- It requires more consumables, such as wire electrodes and shielding gas, which increase the cost of welding.
- It has less control over the weld appearance and quality than TIG welding, as it can create more defects such as porosity, lack of fusion, undercutting, etc.
- It is not suitable for thin materials or delicate workpieces, as it can burn through or warp them easily.
- It is not very effective for welding metals that are prone to oxidation or contamination, such as magnesium or titanium.
TIG vs. MIG Welding : What is TIG Welding?
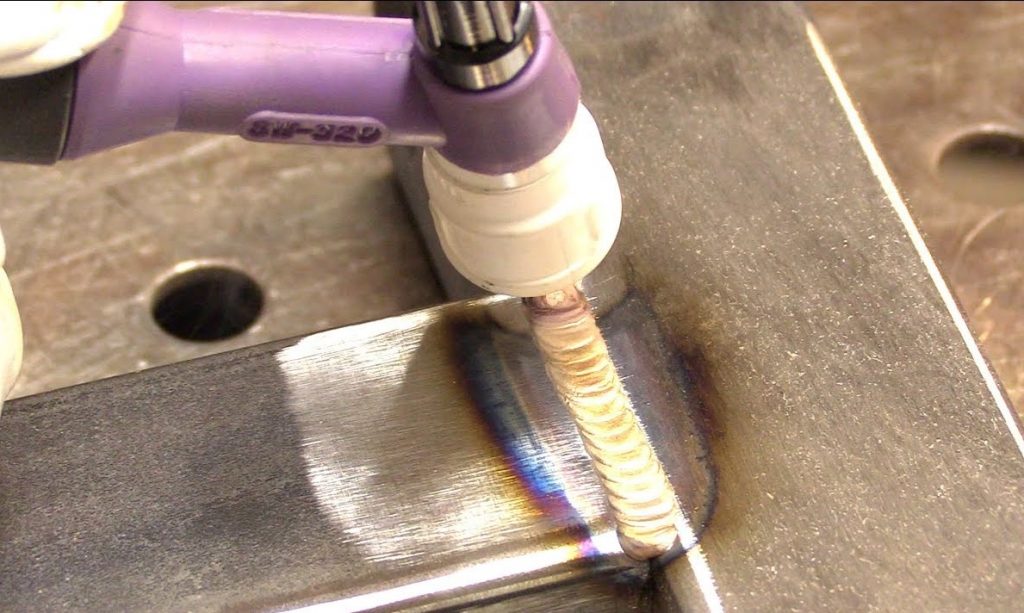

TIG or tungsten inert gas welding is also known as TIG (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding). TIG welding components include a non-consumable tungsten electrode that passes current through the metals to be joined, a computer-controlled controller for timed welding, and a robotic arm assembly to move the weld tip. Unlike MIG welding, TIG welding may or may not use a filler metal for the welding facility.
What does TIG stands for?
TIG welding is an arc welding method, also known as TIG (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding) in which the TIG stands for tungsten inert gas.
TIG Welding Procedure
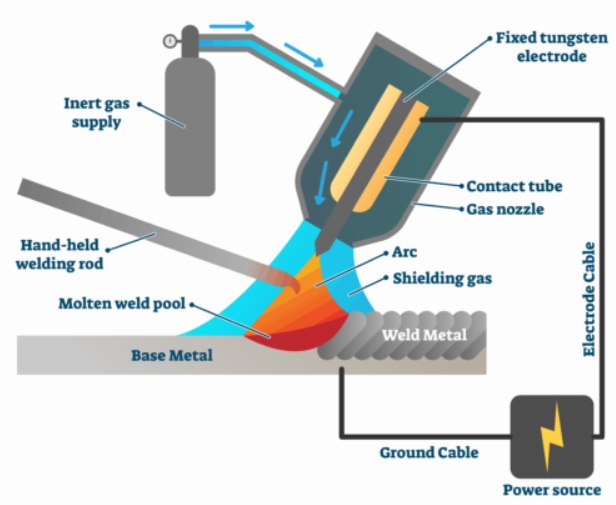
Like the MIG welding robots, TIG welding machines are programmed to perform the welding. During the TIG welding process, dangerous sparks or fillers can burn workers.
Rather than risking damage and providing better consistency, robots are programmed to weld while the human welder checks.
During the process, an inert gas is used to protect the weld area from contamination. Common inert gases used in TIG welding processes include argon and helium.
Unlike the MIG process, TIG welding does not always require a filler, but rather when welding metals with high melting points to avoid cracking.
TIG Welding Advantages
- It produces cleaner and neater welds than MIG welding, with no spatter or slag.
- It has more control over the weld appearance and quality than MIG welding, as it can create smooth and uniform welds with minimal defects.
- It is suitable for thin materials or delicate workpieces, as it can avoid burning through or warping them.
- It can weld metals that are difficult to weld with other processes, such as magnesium or titanium.
- It can create aesthetic and artistic welds that are often used for decorative purposes.
TIG Welding Disadvantages
- It is slower and less productive than MIG welding, as it requires more time and skill from the welder.
- It is harder to learn and perform than MIG welding, as it requires more coordination and concentration from the welder.
- It cannot weld thicker materials with ease, as it requires more heat input and filler material.
- It cannot weld in all positions easily, especially overhead or vertical positions.
- It requires more expensive equipment and consumables than MIG welding,

Applications of MIG Welding vs TIG Welding
MIG welding and TIG welding are both versatile processes that can be used for various applications, depending on the needs and preferences of the welder. However, some general guidelines can help you choose the right process for your project. Here are some of the common applications of each process:
MIG Welding Applications
- MIG welding is ideal for welding thick materials that require high deposition rates and high strength, such as structural steel, pipelines, heavy equipment, etc.
- MIG welding is also suitable for welding thin to medium materials that are not very sensitive to heat or distortion, such as sheet metal, automotive parts, furniture, etc.
- MIG welding is preferred for welding metals that have good weldability and low reactivity, such as carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper, nickel, etc.
- MIG welding is often used for mass production or fabrication work that requires speed and efficiency, such as in manufacturing, construction, or repair industries.
TIG Welding Applications
- TIG welding is ideal for welding thin materials that require low heat input and high precision, such as aerospace components, medical devices, jewelry, etc.
- TIG welding is also suitable for welding medium to thick materials that require high quality and aesthetics, such as sculptures, artwork, custom motorcycles, etc.
- TIG welding is preferred for welding metals that have poor weldability or high reactivity, such as magnesium, titanium, zirconium, etc.
- TIG welding is often used for specialty or custom work that requires skill and creativity, such as in art, design, or hobby industries.
Since fillers can cause weld spatter on the workpiece surface, using TIG welding for direct metal-to-metal welding results in a cleaner and more attractive finish without the need for additional steps such as electropolishing.
How to Choose Between MIG and TIG Welding?
There is no definitive answer to which welding process is better than the other, as both MIG and TIG welding have their own advantages and disadvantages. The best way to choose between them is to consider the following factors:
- The type of metal you want to weld: Different metals have different properties and characteristics that affect their weldability and compatibility with different processes. For example, carbon steel is easy to weld with both MIG and TIG welding, but magnesium is difficult to weld with MIG welding and requires TIG welding.
- The thickness of the material you want to weld: Thicker materials need more heat input and filler material to create a strong weld. MIG welding can provide more heat input and filler material than TIG welding, making it more suitable for thicker materials. On the other hand, thinner materials need less heat input and filler material to avoid burning through or warping. TIG welding can provide less heat input and filler material than MIG welding, making it more suitable for thinner materials.
- The joint configuration you want to weld: Different joint configurations have different shapes and sizes that affect the accessibility and visibility of the weld. For example, a butt joint is a simple joint that can be easily welded with both MIG and TIG welding. However, a fillet joint is a complex joint that requires more skill and control to weld with MIG welding than with TIG welding.
- The quality requirements you want to achieve: Different quality requirements have different standards and specifications that affect the appearance and performance of the weld. For example, a high-quality weld should have no defects such as porosity, lack of fusion, undercutting, etc. TIG welding can produce cleaner and neater welds than MIG welding, making it more suitable for high-quality requirements. However, a low-quality weld can tolerate some defects as long as they do not compromise the strength or functionality of the weld. MIG welding can produce faster and stronger welds than TIG welding, making it more suitable for low-quality requirements.
- The cost factors you want to consider: Different cost factors have different implications on the budget and profitability of the project. For example, a low-cost project should minimize the expenses on equipment and consumables. MIG welding can use cheaper equipment and consumables than TIG welding, making it more suitable for low-cost projects. However, a high-cost project should maximize the value on quality and efficiency. TIG welding can produce higher quality and efficiency than MIG welding, making it more suitable for high-cost projects.
MIG vs. TIG Welding: Comparison between MIG and TIG welding
DIVERSITY
MIG welding is the best choice for your job for several reasons. First, it’s more diverse. While TIG welding can be used on more types of metals, its effectiveness is limited on thicker work.
MIG welding can be used on aluminium, stainless steel and steel and any thickness from 26 gauge sheet metal to heavy construction panels.
MIG welding has this great advantage over TIG, as the wire feed not only functions as an electrode but also as a filler.
It allows thicker parts to be fused without even having to be heated. And since the stuffing is used instead of the melt, two different materials can be welded together during MIG welding.
SPEED
Another reason to choose MIG over TIG is speed. A MIG gun is designed to operate continuously over long periods, making it more efficient and productive than its counterparts. For large industrial companies that require high production speeds, MIG is the way to go. (It’s also suitable for automation). In contrast, TIG welding is a much slower process that focuses on details.
COSTS
As with any production job, time is money. And because the MIG welding process is so much faster, it’s also cheaper. MIG parts are also more readily available and much less expensive than TIG.
EASE
After all, MIG welding is easier to learn and can be perfected after just a few weeks of training. It’s even referred to as the “hot glue gun” of welding – pull the trigger to start or stop welding.
MIG welders can hold and operate the gun with just one hand, which makes it a better option for beginners. TIG welding, on the other hand, is a unique technique in which both hands and one foot have to be used – all with different tasks.
FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions

Is TIG better than Mig?
TIG welds are more suitable for thinner metals and more modest projects because they form solid and reliable welds. MIG is typically more comfortable to manage and is more adapted for beginners. Welders require to have experience with timing and balancing stuff in both hands.
Is TIG welding harder than MIG?
TIG is much more challenging to learn than the other types of welding. It needs a highly skilled operator, as it needs the concurrent use of both hands and afoot. MIG welding is also significantly heavier than MIG.and requires the facade of the workpiece is clean.
What do you use TIG welder for?
TIG welders can be utilized to weld steel, stainless steel, aluminum, Nickel, Magnesium, Copper, and even gold. It is a suitable welding method for welding wagons, bike frames, lawnmower door handles, and more.
What is a MIG welder used for?
MIG welding is an arc welding method in which a consecutive solid wire electrode is fed through a welding gun this stands for metal inert gas.
Conclusion
The answer depends on the function. As mentioned earlier, MIG welding is usually better suited for heavy-duty welding jobs where larger, thicker metal pieces are joined together because of the use of filler material.
However, TIG welding can work wonders when joining smaller metal parts, such as the wires for a custom steel wire basket. Because the TIG process connects two metal parts directly together, no filler material can fall out – meaning less money is spent on welding accessories.
With welding machines, TIG welding can be somewhat less maintenance-friendly as the welding process does not constantly use up the welding electrode. It all depends on what “better” means for you and your welding project.
Since its introduction in the US aerospace industry in the 1940s, what we know today as MIG and TIG welding has become an integral part of amateur and professional welding worldwide.
MIG welding is generally considered to be easier and easier to learn and master than TIG welding. The continuous supply makes the MIG process faster than TIG. Since MIG’s filler means you don’t have to heat the workpiece to form the weld fully, it’s likely better for thicker materials, including heavier structural members.